Archives
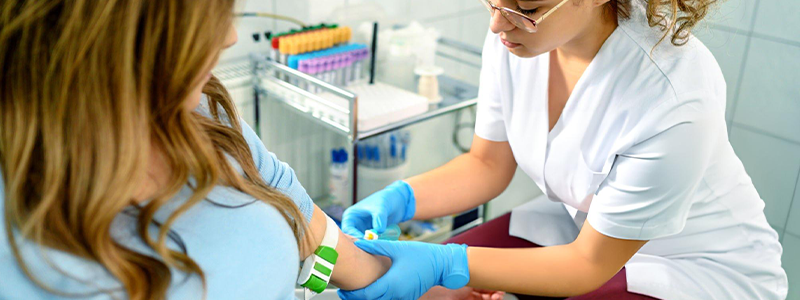
Pregnancy is a miraculous journey filled with anticipation and excitement, but it also comes with a responsibility to ensure the health and well-being of both the expectant mother and her baby. Prenatal care plays a crucial role in monitoring the progression of the pregnancy and identifying any potential issues early on. One integral aspect of prenatal care is the performance of specific lab tests that can provide valuable insights into the baby’s health. In this blog, we will explore the significance of certain lab tests during pregnancy and how they contribute to the overall health of the unborn child.

Blood Type and Rh Factor Testing:
Understanding the mother’s blood type and Rh factor is essential in preventing potential complications. If a mother is Rh-negative and the baby is Rh-positive, there is a risk of Rh incompatibility. This condition can lead to hemolytic disease in the newborn, where the mother’s immune system attacks the baby’s red blood cells. Early detection through blood typing helps healthcare providers implement preventative measures to safeguard the baby’s health.Complete Blood Count (CBC):
A CBC measures various components of the blood, including red and white blood cells and platelets. Abnormalities in these counts can indicate conditions such as anemia or infections, which, if left untreated, could pose risks to both the mother and the baby. Timely intervention based on CBC results can help manage these conditions and promote a healthier pregnancy.Blood Glucose Testing:
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and can affect the health of both the mother and the baby. Regular blood glucose testing helps identify gestational diabetes early, allowing for proper management through diet, exercise, or medication. Controlling blood sugar levels reduces the risk of complications such as macrosomia (large birth weight), birth injuries, and respiratory distress syndrome for the baby.
Serum Screening Tests:
Serum screening tests, including the triple or quadruple screen, assess the levels of certain proteins and hormones in the mother’s blood. These tests can identify the risk of chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome. While these screenings are not diagnostic, they can guide further testing and decision-making regarding potential interventions or additional monitoring.
Ultrasound Examinations:
Although not a traditional lab test, ultrasound examinations are crucial for monitoring the baby’s development. Ultrasounds provide detailed images of the fetus, allowing healthcare providers to assess growth, detect structural abnormalities, and ensure the placenta’s health. Additionally, ultrasounds offer expectant parents an opportunity to bond with their baby and receive reassurance about the pregnancy.
Urinalysis:
A urinalysis is a test that examines the composition of the urine. This test helps identify conditions such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney problems, or gestational diabetes. Monitoring protein levels in the urine is especially important, as elevated levels may indicate preeclampsia, a potentially serious condition that can affect both maternal and fetal health.Group B Streptococcus (GBS) Screening:
Group B Streptococcus is a type of bacteria that can be present in the genital or rectal area of the mother. While GBS is generally harmless to adults, it can pose a risk to newborns during childbirth. Screening for GBS helps healthcare providers determine if the mother requires antibiotics during labor to prevent the transmission of the bacteria to the baby, reducing the risk of infection.Thyroid Function Tests:
Thyroid function is crucial during pregnancy, as imbalances in thyroid hormones can impact fetal development and maternal health. Thyroid function tests, including TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) and T4 (thyroxine) levels, help identify conditions such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Proper management of thyroid disorders is essential for a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Hepatitis B and C Screening:
Testing for hepatitis B and C is important for identifying infections that can be transmitted from mother to baby during childbirth. Chronic hepatitis infections can lead to liver damage, and timely detection allows for appropriate medical interventions to manage and reduce the risk of transmission to the newborn.
Pap Smear and Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Testing:
While these tests are more commonly associated with cervical health, they are essential during pregnancy as well. Abnormalities in cervical cells or the presence of certain strains of HPV can impact the pregnancy and delivery. Early detection and management of any issues related to cervical health contribute to a safer pregnancy and delivery.Other Services
Thyroid test at home
Error: Contact form not found.
You might also like
The Diagnostic Value of CT Scans
Lab test at Home Food Intolerance Doctor at Home Physio
The Vital Role of Vaccinations: Essential for All Ages
Lab test at Home Food Intolerance Doctor at Home Physio
Breastfeeding Awareness Week: Simple Tips for New Moms
Lab test at Home Food Intolerance Doctor at Home Physio

