- admin
- 0 Comments
Archives
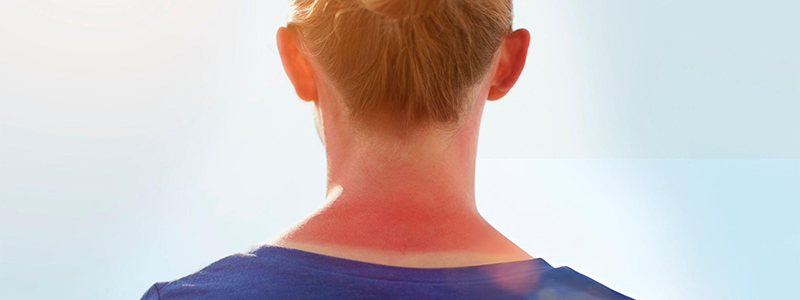
UV Radiation Exposure apart from the Sun
When we think of UV radiation, the sun is often the first thing that comes to mind. However, UV radiation can originate from various sources beyond sunlight. This blog aims to inform readers about the diverse origins of UV radiation and the potential health risks associated with exposure.
Sources of UV Radiation
1.Sunlight
The most common source of UV radiation is the sun, emitting three types of UV rays: UVA, UVB, and UVC. While UVC rays are mostly absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere, UVA and UVB rays reach the surface and can cause skin damage, aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
2.Tanning Beds
Tanning beds are a significant source of artificial UV radiation, primarily emitting UVA rays. Regular use of tanning beds can lead to severe skin damage and significantly increase the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma.
3.Welding Equipment
Welders are exposed to UV radiation from welding arcs, which emit high levels of UVB and UVC rays. Prolonged exposure without proper protection can result in “welder’s flash” or photokeratitis, a painful eye condition.
4.Black Lights
Black lights, often used in entertainment and artistic displays, emit UVA radiation. While the risk of skin damage from occasional exposure is low, prolonged exposure can still contribute to skin aging and potential health issues.
5.UV Lamps
UV lamps are used in various industries, such as for curing inks and resins, water purification, and sterilization processes. These lamps can emit UVB and UVC rays, necessitating protective measures to avoid skin and eye damage.
6.Medical and Dental Equipment
Certain medical and dental procedures use UV radiation for sterilization and treatment purposes. UV light is effective in killing bacteria and viruses, but appropriate shielding and protective measures are crucial to protect patients and healthcare workers.
Health Risks of UV Radiation Exposure
Exposure to UV radiation can lead to several health issues, including:
Skin Damage: UV rays can cause sunburn, premature aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Eye Damage: Prolonged exposure can lead to cataracts, photokeratitis, and other eye conditions.
Immune System Suppression: Excessive UV exposure can weaken the immune system, reducing its ability to fight off infections.
Protective Measures Against UV Radiation
Sunscreen: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, even on cloudy days and during winter.
Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses that block UV rays.
Avoid Tanning Beds: Opt for safer alternatives like self-tanning lotions or sprays.
Workplace Safety: Use protective gear such as UV-blocking goggles and face shields when working with UV-emitting equipment.
Understanding the various sources of UV radiation and the associated health risks is essential for effective protection. While the sun is the most well-known source, artificial sources like tanning beds, welding equipment, and UV lamps also pose significant risks. By adopting protective measures, we can minimize our exposure to harmful UV radiation and safeguard our health.

Other Services
Thyroid test at home
Error: Contact form not found.


